The Smart City Delhi mission of NDMC is to “be the global benchmark for a capital city”.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced the commencement of the Smart City Delhi Mission in 2015, along with many other cities. The project intends to boost economic growth and the quality of living for Indian citizens. According to 2021 data, 35.3% of India’s population resides in cities, and by 2030, around 40% of Indians are projected to live in cities, contributing 75% of the country’s GDP. The Smart City initiative aims to raise living standards in 100 cities and towns.
The New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC) was chosen as one of the first 20 cities under the Smart City Mission by the Indian Ministry of Urban Development. Based on stockholder discussions and a questionnaire survey, New Delhi, consisting of Connaught Place and adjoining areas of estimated 550 acres, has been chosen for the maintenance and rehabilitation model of development. Smart City Delhi began with the underlying need to transform every city in India as a “World Class Urban Area.”
Table of contents
Delhi Smart City Objectives
The key objectives of Smart City Delhi‘s mission are –
- Access to sustainable urban mobility options such as smart parking and non-motorized vehicles (NMVs) to improve mobility via efficient traffic management
- Focusing on the requirements of transgender, disabled, children, and women
- The enhancement of quality of life through citizen-focused design and planning
- Focus on social development by improving healthcare and education through the use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
- Setting international standards to satisfy citizens’ expectations
- Access for residents to basic infrastructure facilities, such as 24×7 clean water and power supply
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to improve the air quality in Delhi
Features of Smart City Delhi
The following are several prominent features of growth and expansion in Smart City Delhi –
- Supporting mixed land use in area-based projects, which entails creating unforeseen areas with several complementary purposes and activities located adjacent to one another. To respond to change, the State will provide certain flexibility in land use and building ordinances.
- Increase in the number of housing options available to all citizens.
- Developing walkable communities to ease traffic, air clean-up, conserve resources, strengthen the local economy, foster community connection, and improve security. The road system is built or upgraded to accommodate automobiles and public transportation.
- Conserve and build parks, playgrounds, and amusement areas to improve the life quality of citizens, decrease the impact of urban heat effects, and encourage eco-balance.
- The provision of transportation alternatives, including public transportation and Transit-Oriented Development (TOD).
- Rendering government more accessible to the public and cost-effectively relying on online services to promote transparency and accessibility. Particularly when employing mobile devices to lower service costs and provide services without requiring a visit to a municipal office.
- Creating online discussion forums to hear from people, receive their comments, and use online monitoring of programmes and activities via virtual site visits.
- Offering the city a distinct character based on its primary economic activity, including local food, health, education, arts and crafts, culture, furniture, textiles, and dairy products.
- Improving infrastructure and services in area-based development by utilising smart solutions. For instance, reducing the risk of disasters, employing fewer resources, and offering affordable services.
Delhi Smart City Projects
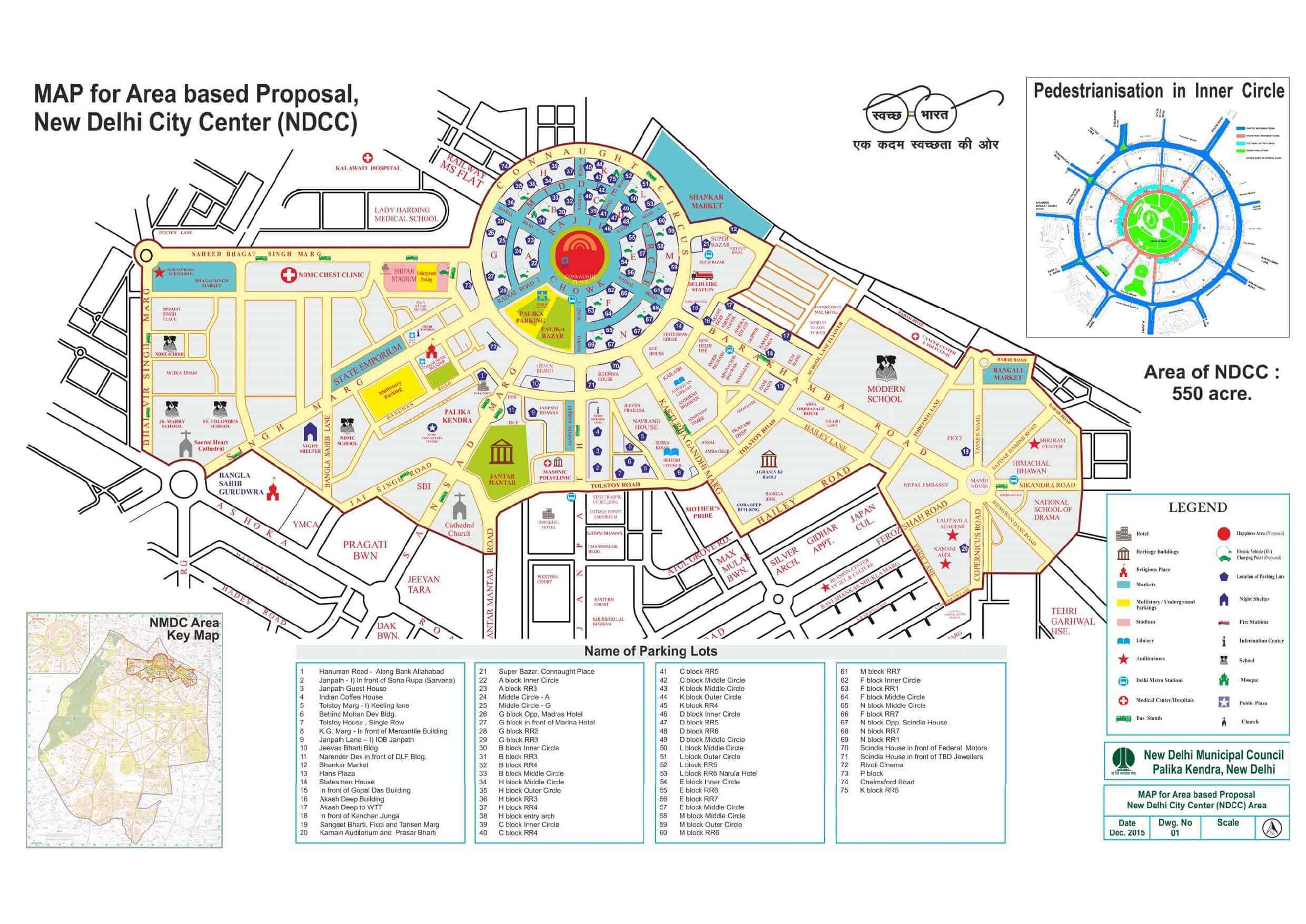
Source@ https://smartcity[dot]ndmc[dot]gov[dot]in
Based on the Economic Survey of Delhi conducted for 2021–2022, there were 106 projects planned for Smart City Delhi. However, 86 of the projects have been developed and constructed, and six remain in the Detailed Project Report (DPR) stage.
The following table showcases the different Pan-City projects for Smart City Delhi along with the estimated prices for each project –
| S. No. | PAN-CITY Projects | Project Price |
| 1 | E-governance | Rs. 10 Crores |
| 2 | Smart Grid and Energy Management | Rs. 958 Crores |
| 3 | Smart Grid Implementation | Rs. 528 Crores |
| 4 | Solar Power (40 MW) Projects | Rs. 430 Crores |
| Smart Water Management | ||
| 5 | Pan-Smart Water Management Waste Water Management |
Rs. 190.42 Crores |
| Smart Education | ||
| 6 | All NDMC schools integrated with e-learning | Rs. 35 Crores |
| 7 | Centralised electronic health records for students | Rs. 10 Crores |
| Smart Health | ||
| 8 | Interconnect a cloud-based electronic healthcare system with all public healthcare amenities | Rs. 20 Crores |
| 9 | Centralised hospital assistance for Economic Weaker Sections to access private beds. In addition, the provision of transportation services for transfer to private hospitals | Rs. 1.75 Crores |
| 10 | Medical Services Online | Rs. 3 Crores |
source@ https://smartnet[dot]niua[dot]org
The following table showcases the different Area-Based Development projects for Smart City Delhi along with the estimated prices for each project –
| NDMC Smart City Delhi Projects | ||
| S. No. | Area Based Development (ABD) | Project Price |
| Urban Mobility & Smart Parking | ||
| 1 | Para-transit facilities such as Pelican crossing | Rs. 5 Crore |
| 2 | Last-mile connectivity based Electric Vehicles | Rs. 25 Crore |
| 3 | Electric Vehicle charging station at parking area | Rs. 1 Crore |
| 4 | Cycle Tracks Integrated via Apps | Rs. 2 Crore |
| 5 | e-surveillance and e-challans against traffic offences | Rs. 5 Crore |
| 6 | Intermediate Public Transport Parking | Rs. 1 Crore |
| 7 | Smart City Bus Stops | Rs. 1 Crore |
| 8 | Automated multi-level car-parking | Rs. 190 Crore |
| 9 | Smart City Parking with sensors | Rs. 6 Crore |
| 10 | Inner Circle Connaught Place Walkway | Rs. 20 Crore |
| 11 | Common Service Utility Duct with Sensors | Rs. 150 Crore |
| 12 | Installation of Smart poles with LEDs, communication infrastructure, Wifi access, sensors for air quality and noise pollution | Rs. 25 Crore |
| 13 | Command and Control Centre | Rs. 15 Crore |
| 14 | Happiness Areas | Rs. 35 Crore |
| 15 | Happiness area for the citizens’ cultural and social requirements | Rs. 10 Crore |
| 16 | Renovation of CP’s Gole Market – Adding an Interactive Museum on the History of Indian Civilization |
Rs. 25 Crore |
| 17 | Transforming subways into vibrant spaces such as installing ATMs and pet-adoption centres | Rs. 5 Crore |
| 18 | Smart Digital Screen for Traffic Information, SocialMessages,Alerts, Cricket News, and Advertisements | Rs. 20 Crore |
| 19 | Rooftop solar panels | Rs. 105 Crore |
| 20 | Installation of Rooftop solar panels of 7.5 MW in public buildings | Rs. 52.5 Crore |
| 21 | Installation of Rooftop solar panels of 7.5 MW in Private Sector buildings | Rs. 52.5 Crore |
| Municipal Solid Waste Management | ||
| 22 | Waste bins with Geotagging | Rs. 1 Crore |
| 23 | The provision of new waste-bins | Rs. 1 Crore |
| 24 | Automatic sewer cleaning machine | Rs. 14 Crore |
| 25 | Enhancing current automated road cleaning equipment | Rs. 16 Crore |
| 26 | Transforming Green waste to Smart Gas plant | Rs. 8.6 Crore |
| 27 | Transforming Public Toilets into Smart Public Amenities Centres | Rs. 4.5 Crore |
| 28 | Inclusion in financial, identity, ticketing, and access | Rs. 5 Crore |
| 29 | Introducing signature initiative to the city’s Identity and Culture | Rs. 3 Crore |
| 30 | Gateway to the World: On-street Live Video Conferencingbetween people of Delhi and multiple Global Cities | Rs. 3 Crore |
| 31 | Delhi International Festival | NA |
| 32 | Global Capital City Award | NA |
| 33 | Behavioral transformation | Rs. 5 Crore |
source@ https://smartnet[dot]niua[dot]org
Don’t miss It!
| Smart City India | Smart Cities India Mission & Projects |
| Smart City Dehradun | Dehradun Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Bhopal | Bhopal Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Ranchi | Ranchi Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Dholera | Dholera Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Bangalore | Bangalore Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
The idea of a Smart City is contingent on a variety of variables. It entails focusing on transportation improvements, better health services, a clean environment, and executing a thorough examination of the city. As a result, there are various methods to envision the strategy for Smart City Delhi. The five areas that should be addressed include providing contemporary infrastructure, sustainable amenities, technology and development, unique ways to maintain a hygienic environment, and other social services for the community. The first stage is to build a Smart City Delhi map that shows the city’s priority areas.
The following map below depicts the points of all the Smart City Delhi projects –
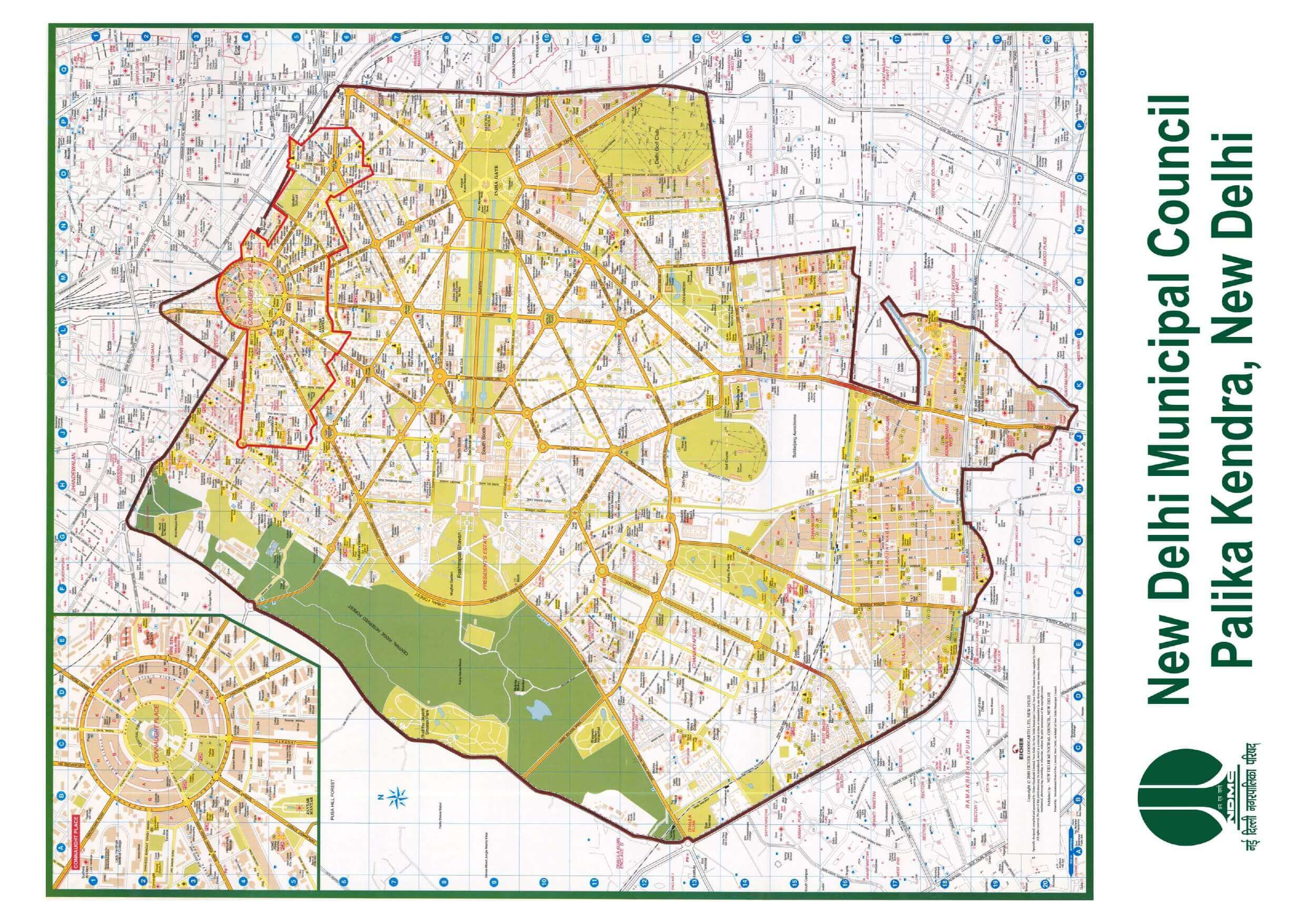
source@ https://smartcity[dot]ndmc.gov[dot]in
Current Status of Delhi Smart City Mission
With 106 projects in hand under Smart City Delhi Mission, the city has completed 86 projects as per March 2022. Some of the completed projects of Smart City Delhi are –
- Smart Parking in various NDMC areas
- Solar rooftops are installed on around 28 government buildings
- The National Museum of Charkha was built opposite Khadi Gramodyog Bhavan in Connaught Place in 2017
- Happiness Areas in different parts of Delhi such as Kautilya Marg, Yashwant Place, Ambedkar Vatika, Nyay Marg, and more
- Bio-Methanation Plant installation at Laxmi Bai Nagar
- Facade Lighting at Palika Kendra
- Several Electric Vehicle (EV) charging stations are installed in different parts of Delhi
- Around 55 smart poles in Connaught Place are installed
- Transformation of Smart Public Centres such as water vending machines, cash machines, digital clinics, and public washrooms
- Health ATM at Palika Kendra Dispensary
Delhi Smart City Citizen Services
A state-of-the-art citizen application for Delhi residents by the NDMC is NDMC-311. The application offers a wide range of unique features that give users access to several public services. Listed below are the features offered by the NDMC-311 application –
- Citizens can receive comprehensive information about the NDMC. They can find information on the city’s history, mission, departments, forthcoming events, and more.
- Helpline 24×7 for emergency departments such as NDMC control room, fire, ambulance, disaster management, and women helpline.
- Citizens can pay water, electricity, property tax and estate bills with the Quick Pay feature on the app.
- The app helps you find nearby locations and areas and other amenities such as public washrooms, police stations, metro stations, petrol pumps, hospitals, markets, tourist locations, and more.
- Citizens can complain about issues related to NDMC Maintenance and Electricity Department. They can attach pictures and comments in the complaint section.
- Real-time information and updates on traffic and parking in different areas of Delhi.
Are You Planning to Shift? We Provide Packers and Movers Services in Delhi!
FAQ’s about Delhi Smart City
Q1. Is Delhi on the Smart City list?
Delhi is part of the Smart City list that includes 100 other cities under the Smart City Mission.
Q2. Why is Delhi called a smart city?
Delhi will be considered a Smart City as it will have top-notch infrastructure, 24-hour power supply, wi-fi connectivity, and install green technology. It will also implement water conservation techniques such as rain harvesting and waste management.
Q3. Is Delhi a metro city?
Yes, Delhi is a metropolitan city with an urban population, modern infrastructure, top-notch amenities and services for citizens, education and employment opportunities, and interconnected transportation facilities.
Q4. When did Delhi become a Smart City?
In 2016, the New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC) was chosen as a Smart City under the Smart City Mission by the Indian government.