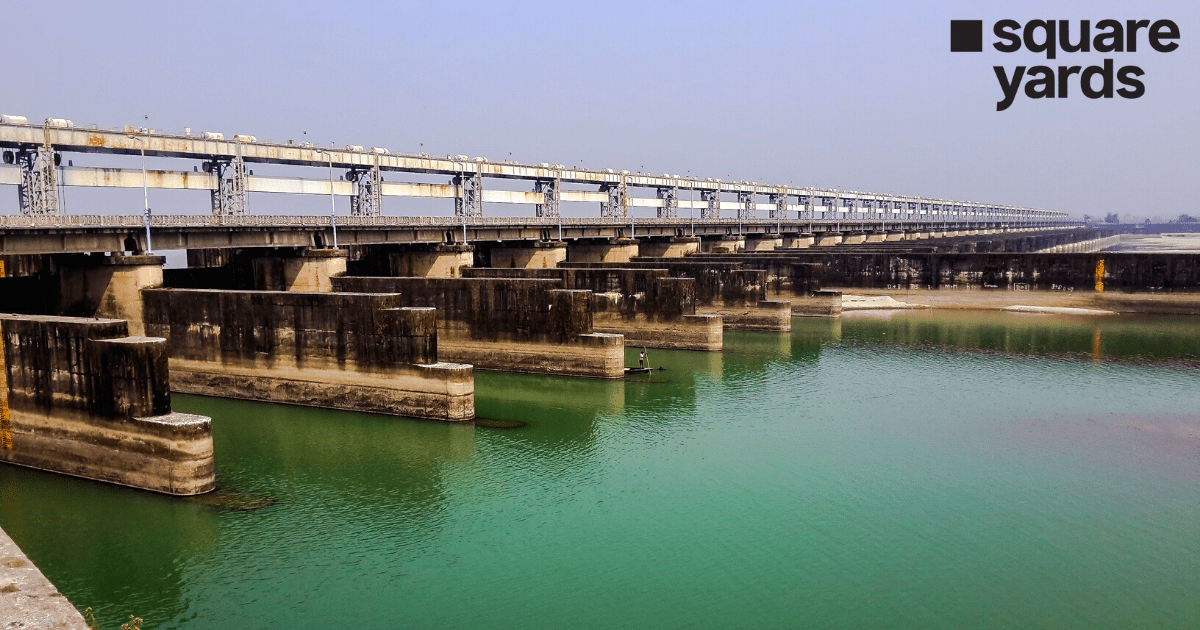
The Farakka Barrage was constructed in 1976 in West Bengal to divert the flow of the Ganges. Amidst various hassles that ensued during and post the construction of the project, it led to improvement in the water levels of the state. Additionally, the dam led to the gradual improvement of the Kolkata Port and reduced the salinity levels of the water.
About Farakka Barrage
In the year 1976, the Farakka Barrage at the apex of the delta region and in the Indian territory of West Bengal started diverting the Ganges in the South of India. The Indian Government raised a question about how the hydrological changes in the preceding century have caused the Ganges water diversion from the Kolkata port which has led to the intrusion of seawater and deposition of silt over time. Further, the dam was constructed to improve the situation of Kolkata by flushing and diverting the seawater while raising the water level.
However, the Bangladeshi Government emphasised on the deprivation of the crucial source of water in the southwestern part of the country due to this Barrage project. After 20 years of construction, in 1996, both Indian and Bangladeshi Governments decided to resolve the issue by signing a treaty which stated the division of Ganges waters proportionately between both the countries.
Birth of Farakka Barrage
The construction of Farakka Barrage was commenced in the year 1962 and was finalised in 1970 with the cost of a whopping $208 million. In the year 1975 on 21st April, the operations for the bridge were officially started.
The Indo-Bangladesh Water Sharing Treaty
Both the Bangladeshi and Indian Governments signed a treaty for sharing the waters of the Ganges during the dry season spanning from January 1st to May 31st on 12th December 1996. The previous agreement made between the two countries was short-term, but this was for 30 years. It also has the extension provision if the parties involved agree to it. As per the specifications of the treaty, a formula is used to compute the water share division. It stated that 35,00 cusecs of water will be provided on both sides with a segment of 10 days, alternatively from 11th March to 10th May. However, if the flow of the water reaches below 50,000 cusecs, the treaty says that the situation will be treated as an emergency with the immediate requirement of consultations from India and Bangladesh.
In the 1977 agreement, it was stated to deliver 34,500 cusecs of water and that India will put its best foot forward in protecting the flow of water at the Farakka Barrage. In addition, the treaty has a provision of a review at the end of five or two years if either of the parties requires it.
Impact of Farakka Barrage Bridge on Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, as per the perception, the salinity levels have increased, navigations are hindered, the fisheries are contaminated and a threat to public health and water quality prevails because of this Barrage Project. Further, the increased salinity levels and the decrease in levels of soil moisture have led to desertification. However, This Barrage remains to be one of the crucial aspects of mutual relations between the countries.
Farakka Barrage Township
In the Farakka CD Block, Farakka Barrage Township is a census township which is in the Jangipur subdivision of Murshidabad district in the state of West Bengal. This Township Murshidabad is spread across an area of 3.7 square kilometers with 70.3-kilometer roads which have both open and closed drains.
Functions of Farakka Barrage Murshidabad West Bengal
- To ensure that the decided Ganges waters are diverted to the Bhagirathi-Hooghly River system to preserve and improve the conditions of the Kolkata Port.
- To enhance the system of navigation for the National Waterway No.1 which is operational between Haldia and Allahabad.
- To reduce the salinity in the water as well as to improve and increase the availability of potable water for the city of Kolkata and neighbouring areas.
- To provide the northeast region of India, a link for surface communication with the rest of India including Nepal and Bhutan through the Rail cum Road bridge which is over this Barrage.
- To release the waters of Ganges to Bangladesh as per the specifications of the 1996 treaty during the lean season.
- To protect the ones dwelling on the countryside and their land along with the public properties like bridges and roads by keeping a check on the soil erosion at the Ganga-Padma River for the Murshidabad and Malda districts.
- To ensure the supply of water for the NTPC operated Thermal Power Plant at Farakka.
Specifications of the Farakka Barrage
| Farakka Barrage Length | 2,304 metres |
| Farakka Barrage Distance | 18 km |
| Farakka Barrage Construction Cost | ₹156.25 Crores |
| Farakka Barrage Gates | 109 |
| Farakka Barrage Opening Year | 1972 |
| Farakka Barrage Impounds | Ganges River |
Though the Farakka Barrage is known to have certain environmental impacts on the country, it still remains to be the bridge between the mutual relations of Bangladesh and India.
Don’t Miss Out
FAQs
Q. Where is the Farakka Barrage?
Farakka Barrage is located in the district of Murshidabad.
Q. What is Farakka Barrage Project?
Through the Farakka Barrage Project, Ganges waters are diverted to the Bhagirathi-Hooghly River system to preserve and improve the conditions of the Kolkata Port.
Q. Which is the highest dam in India?
Tehri Dam is the highest dam in India.
Q. How many gates does Farakka Barrage have?
There are 109 Farakka Barrage Gates.
Q. How many national highways have crossed Farakka Barrage?
Farakka Barrage crosse the National Highway 12 from all the national highways in India.