As we know that GSTR 1 contains all the details about the sales of a business and GSTR 2 has all the information about all the purchases made in a certain month. But do you know about GSTR 3? Well, I think not properly.
Therefore, in this blog, we will discuss the GSTR 3 form. We will update you about how it is filed, what are the eligibility, due date, and late penalty fee.
GSTR 3 is an automatically generated form. It is a summarization of all the data filed in both form GSTR 1and GSTR 2. GSTR 3 is filed monthly from the 16th of any month to the 20th of the upcoming month.
Here is more for you to explore about GSTR 3.
What is GSTR 3?
GSTR 3 is a document that includes all the information about the transactions, purchases, sales, and stocks interstate moment for a particular month. In other words, we can say that GSTR 3 is a monthly return that has all the details about your monthly expenditure in an appropriate summarized manner.
GSTR 3 is an auto-generated information pulling form from GSTR 1 and GSTR 2. And, is filed during the same tax period as of GSTR 1 and GSTR 2.
Who should file GSTR-3?
Every businessperson or an individual who is registered as a GST dealer is required to file GSTR 3. It is important to file GSTR 3 every month and is independent of the business activities. What we meant to say is, even if there are no activities during that month, an individual has to file GSTR 3. Here is the list of registered persons who don’t have to file GSTR 3:
- The Input Service Distributors
- The Composition Dealers
- The person is Non-resident but a taxable person
- All the persons are liable to collect TCS
- All the persons who are eligible for TDS deduction.
- And, in the interim of all the online information and database access (OIDAR), a person who pays the taxes by themselves as per the section 14 that falls under the IGST Act.
What is the importance of GSTR-3?
GSTR 3 is important because it displays the amount of GST liability for the month. Therefore, it is necessary for the taxpayer to pay and file the tax return.
What if GSTR-3 is not filed on time?
If someone by mistake forgets to file or register for GSTR 3 then they won’t be able to file for GSTR 1 in the upcoming month. Therefore, the late filing will have a contradictory effect and will lead to heavy fines and penalties.
What if the GSTR-3 filed after the due date?
If there is delay in filing GSTR 3 then you have to pay a certain fee for being a late depositor with 18% annual interest. This 18% interest will be calculated by the taxpayer on the outstanding amount of tax to be paid.
Here are the following factors if you are not able to file GSTR 3 on time.
- A penalty of Rs. 100 from the next day till the day GST return is filed. It will be Rs. 100 under CGST and SGST i.e.Rs. 200 each day.
- The penalty is payable for the time the taxpayer failed to return the GST with a maximum limit of up to Rs. 5000.
- GST won’t be filed for the next month if the previous month GSTR 3 is not filed.
- And, if the taxpayer fails to file GSTR 2 on the 15th of the month then he will not be able to file GSTR 3 on the 20th of the same month.
Therefore, late GST return filing has its own consequences that include heavy fines and penalties.
How can an individual revise GSTR-3?
Once a taxpayer filed the GSTR 3 then there is no process to revise it. In case, the taxpayer made any mistake then that will be revisable only in the next month’s GSTR 1 and GSTR 2 returns.
In nutshell, the direct revision of GSTR 3 is not applicable because it is an auto-generated form that cancels all the possibilities of editing the form.
How to reconcile both GSTR-3 and GSTR-3B?
- The GSTR 3b form was introduced by the CBEC for the months of July and August in the year 2017. Also, GSTR 3 was also filed for the months of July and August in the year 2017.
- Moreover, the filings of GSSTR 3 and GSTR 3b are different from each other and the system will update this difference between both the forms on its own.
- And, if the real liabilities are higher in GSTR 3 than those compared to GSTR 3b then the taxpayer has to pay the extra sum of money along with some interest on the extra amount.
Note: GSTR-3 must be filed only after paying the entire tax liability otherwise it will not be interpreted as a correct return. And, if a taxpayer filed an invalid return and wants to pay the remaining liability later then he has to file the second part or Part B of GSTR-3 again.
How to file GSTR 3b?
The details of GSTR 3 are divided into fifteen subheadings as per the format described by the government of India. To make the process easy and understandable we have explained each section with all the data required to file GSTR 3.
Let’s start,
- Provide GSTIN
In case any taxpayer doesn’t have any GSTIN then he or she can use their provisional id as well.
- Name of the Tax paying Individual
The name of the tax paying person is autogenerated and displays both trade & legal names.
Now, the tax paying person has to maintain the month and year for which he or she is filing the GSTR 3.
Moving ahead, GSTR 3 is divided into two parts. PART A and PART B. PART A is auto-generated from GSTR 1 and GSTR 2 whereas, PART B has to be filled manually.
PART A (Auto-Generated):
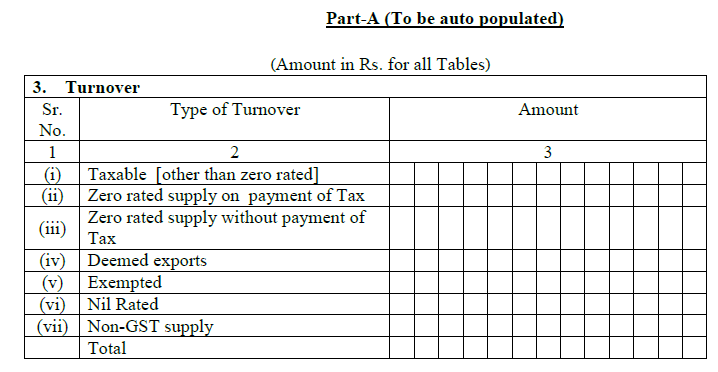
- Mention the Turnover
One has to mention the overall turnover of all supplies that will further be divided into different parts between the following:
- Taxable Turnover (must include normal sales for both non-registered and registered buyers).
- Zero supply with payable tax (include exports that will be paid by using IGST and later come back as a refund.).
- Zero supply without payment of tax (includes exports paid using bond/LUT).
- Exports items sold to SEZ and do not leave the country in reality.
- Goods or services that do not draw GST.
- Goods or services that draw 0% GST.
- Supplies that do not fall under the category of GST.
- Outside supplies
It has all the information from your GSTR 1.
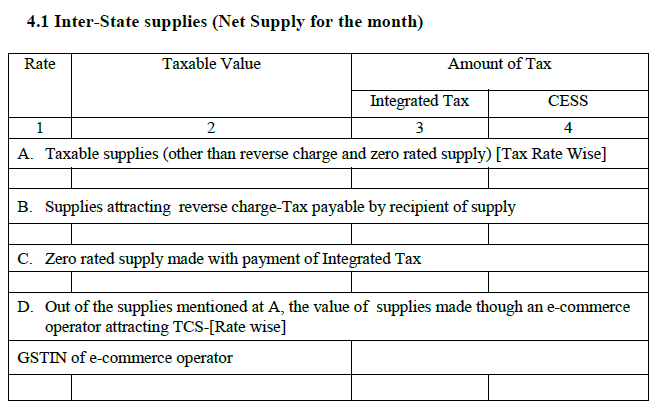
4.1 Inter-State supplies for the month:
- Supplies that are taxable
- Supplies that attract reverse chargeable-tax that is further payable by the beneficiary of supply.
- Zero supply when the payment is made by IGST.
- The worth of supplies made using an e-commerce operator.
Note:
- Supplies with zero-rated payment of taxes will not be included.
- Changes in supplies that are made under a reverse charge.
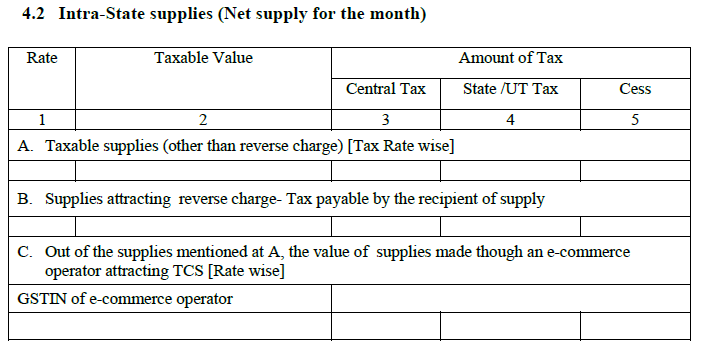
4.2 Intra-State supplies for the month:
It is similar to inter-state sales except that this will have details of intra-state sales.
4.3 Effect on Tax effect in respect of outward supplies after the amendments:
It will have all the information about the changes made by you in your invoice due to any reason. For example – If the amount is changed then there will be an effect on the payable tax to the Indian government. Therefore, under this heading, the form keeps the track of changes made in the invoice.
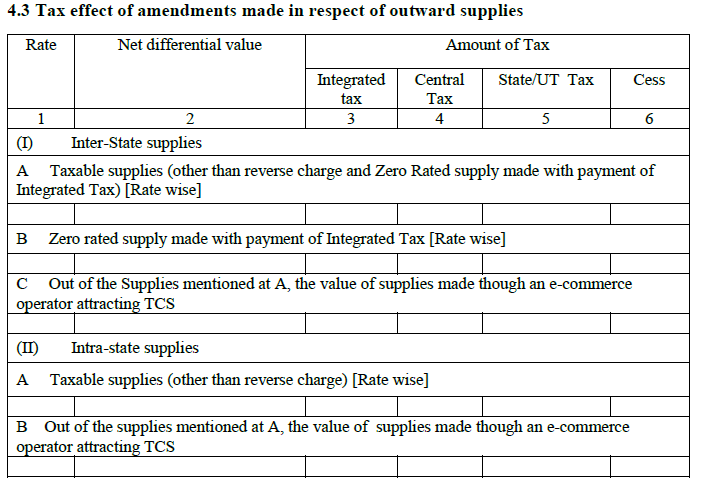
- Inside supplies
The information will be taken directly from GSTR 2 form:
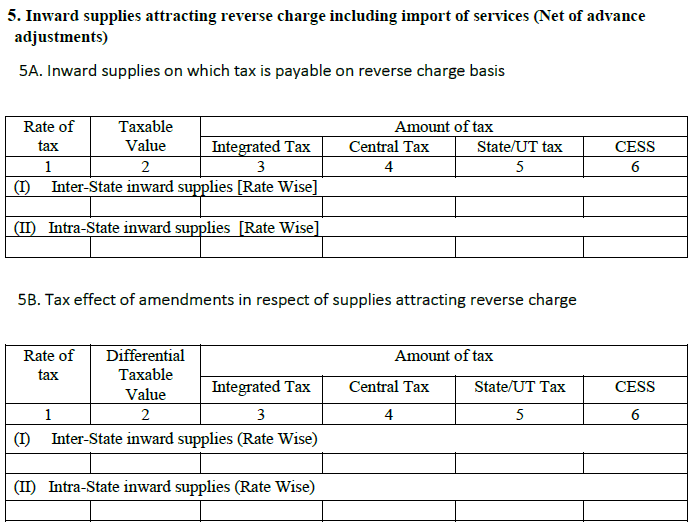
5.1. Inward supplies – payable tax on a reverse basis:
Here you will see the purchases on which the reverse charges are applicable. You can see both interstate and intrastate sales. The liable tax due to reverse charges in this section, includes net invoices, debit or credit notes, advances paid and adjustments payments made in advance.
5.2. Tax effect after making changes in supplies that draw reverse charges:
It will display you all the charges made on your purchases and thus have reverse charges applicable on them. In case, the amount varies then the sum of ITC will also vary that will further change the payable tax. Therefore, this section helps in keeping the track of changes made in the invoices and their direct effect on total payable tax.
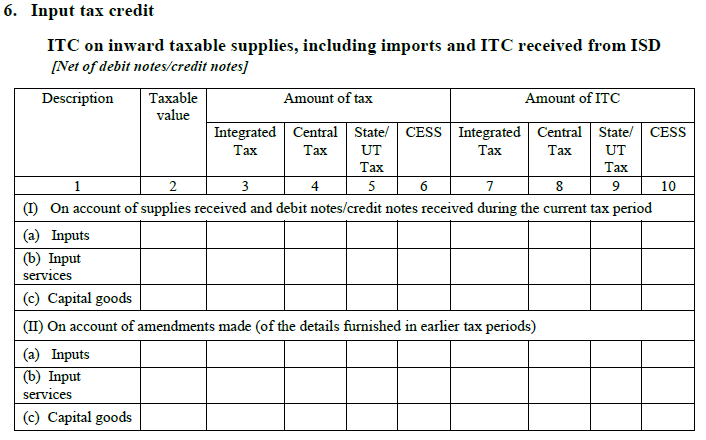
- The Input tax credit
Part I:
It will give you a summary of the available ITC of the month. The ITC will be displayed here separately – Inputs (raw materials), Input Services (consulting fees, etc), and Capital Goods (laptop, etc).
Also, the ITC received by ISD will also be displayed here after changing the debit and credit notes as per the requirement.
Part II:
It contains all the changes made in the earlier month’s and their impact on ITC.
Note: ISD is an acronym of Input Service Distributor.
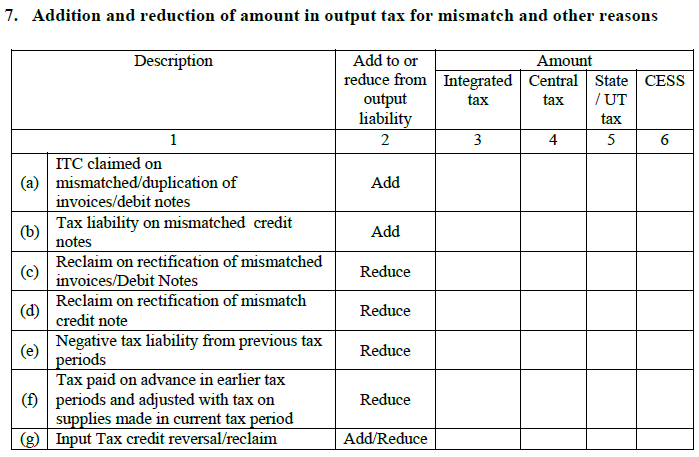
- Addition or subtraction of amount from output tax due to different other reasons
All the information contained under this heading will be sourced from GSTR 2.
7.1. Claiming on ITC in case it is mismatched or duplicate of invoices: If there is a mismatch in invoices, then there may be double claiming of ITC. And, the double ITC claimed from duplicate purchases, there will be an impact on the invoice (reversed and added for tax liability).
7.2. There will be tax liability if credit notes are mismatched: Inaccurate credit notes published by you can lead to incorrect ITC results. Therefore, more ITC will be claimed and added further as your tax liability.
7.3. Redemption of mismatched invoices: In this case, the mismatch will lead you towards lower ITC. You are entitled to pay more ITC but the additional amount will be decreased from the total output tax liability.
7.4. Redemption of mismatch credit notes: In this situation, lower ITC will be claimed and overall output tax liability will decrease.
7.5. There will be negative tax debt due to previous taxes: It happens because of the huge amount of tax paid in the preceding months and thus it will be reduced from your overall liability of tax in the present month.
7.6. The tax paid in advance earlier will be adjusted with the taxes made on the supplies in the current period: It means that the tax is paid as an advance payment made in the previous months for supplies (received during the current month).
7.7. Reversal of Input Tax credit: It means that the ITC is again claimed for any other purposes.
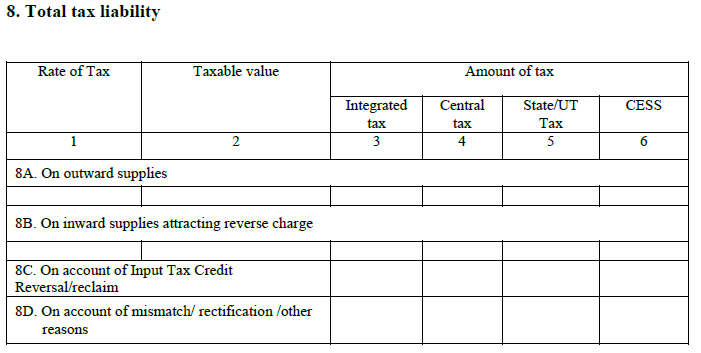
- The Overall tax liability
It will help in calculating the tax liability under different sections of tax like CGST, SGST, and IGST. Here it is:
8.1. Tax on outside supplies – Payable on normal sales along with inter-state sales.
8.2. Tax on inside supplies beneath reverse charge.
8.3. Tax on basis of ITC re-claims – Additional tax payable or reduction due to the reversal ITC.
8.4. Tax on basis of mismatch or rectification or other reasons.
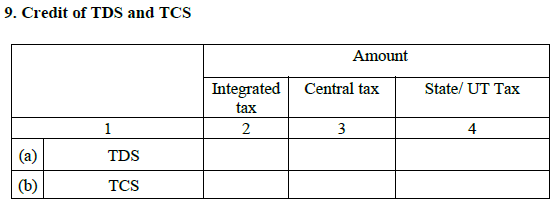
- The TDS and TCS credit
This section will display all the information of TDS and TCS, that is paid by the tax paying person. Also, the amount deduction will take place from the overall liability of the tax amount just paid by you.
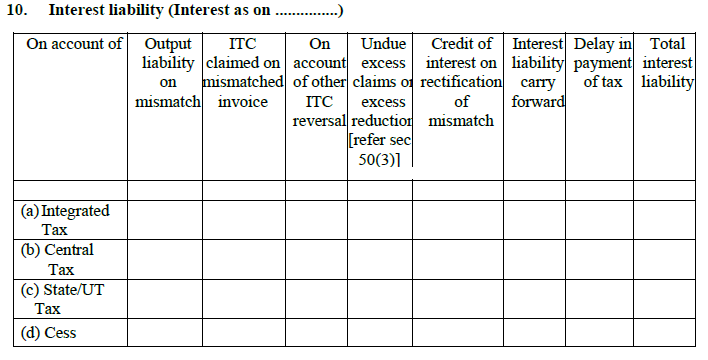
- Interest liability
Whenever there is a delay from the taxpayer’s side in filing the return, there will be chargeable interest that they have to pay. The interest is 18% annually and determined by the taxpayer’s outstanding tax that he or she has to be paid.
Under this heading, one can see the reasons and the amount of the applicable interest. It is further bifurcated under CGST, SGST, IGST, & Cess.
10.1. If the output is mismatched: The tax liability has been increased because of the changes made in the sales invoice.
10.2. Claiming ITC on a mismatch invoice: Due to making changes in the purchase invoices, if the liability of your tax is increased. Then you have to pay the interest on the increased amount.
10.3. Other ITC reversals: When your ITC claim is reversed and increases your tax liability. Therefore, you have to pay the interest now.
10.4. Excess undue claims or reduction: If by mistake you have asked for extra ITC and now you need to pay the interest as well.
10.5. Interest credit on redemption of mismatch: When you paid the interest on mismatch and later it is reversed back into your account.
10.6. Interest liability: Interest that you will pay partly and the main sum of money will be forwarded into the next month.
10.7. Delay in paying tax: Payable due to late payment or late filing of returns.
10.8. Cumulative interest liability: Displays the complete payable interest under different sections such as – CGST, SGST & IGST.
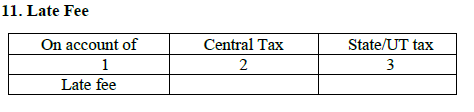
- Late Fee
If a taxpayer fails in filing a return then a late fee is chargeable along with the interest. The late fee charge is Rs. 100 every day, The maximum charges will be Rs. 5000 only. After that severe action will be taken.
Note: No late fee penalty is applicable on IGST.
Part B
This section of the form will be entirely filled manually by the tax paying person
- Tax payable and paid
As a taxpayer, you have to fill all the columns with exact amounts and in the correct format.
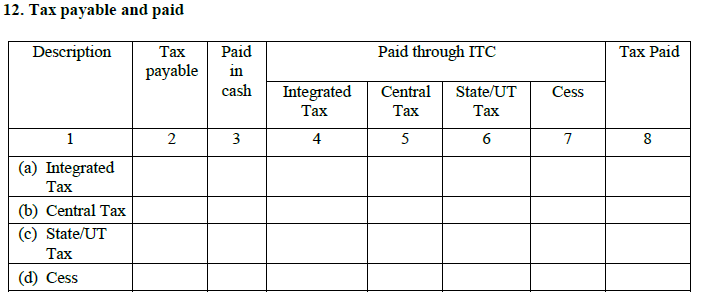
- Different payable amounts apart from tax
You have to fill the total amount which has to be paid by you and the amount that has to be paid under interest and late fee.
Note: No late fee for IGST.

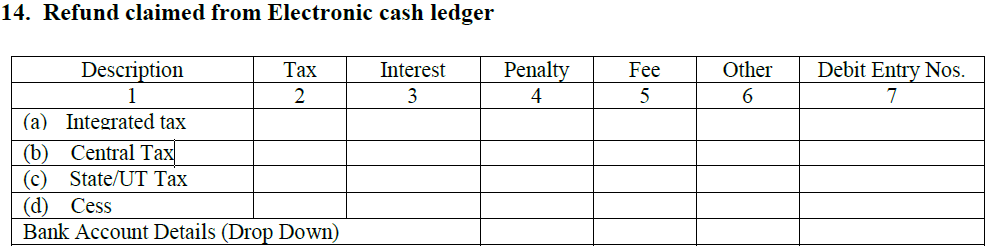
- Claiming the refund from E-cash ledger
If it is found later that the tax paid by you is greater than the actual amount then the sum difference will come back to your account.
Note:
- The refund from the cash ledger is only applicable when all the liabilities related to the return have been released for the month.
- When the refund is claimed, it will display the result in a debit entry in the e-cash ledger while filing GSTR-3.
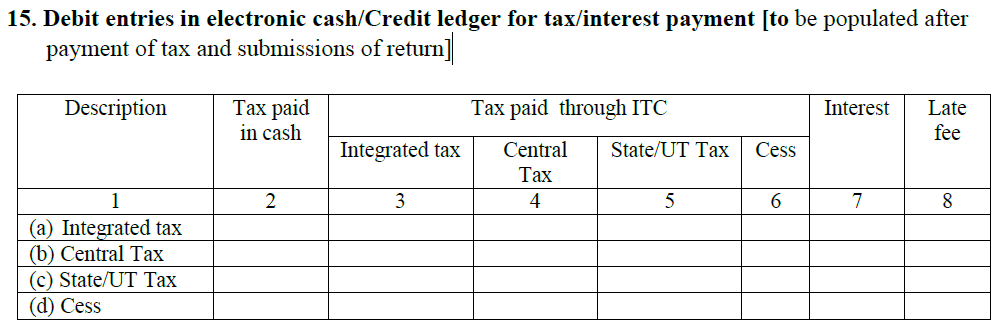
- Debit entries in e-cash or credit ledger for tax or interest payment
- This section will be auto-filled once you pay taxes and submit all your returns.
- The last section of the form is the declaration that all the data mentioned in this form is correct and appropriate.

What are the key components of GSTR 3?
Here are some key takeaways from the GSTR 3 filing.
- GSTR 3 works as an agent that automatically generates and summarizes all the information from GSTR 1 and GSTR 2.
- All the information will be updated in real-time. Information such as Tax Credit Ledger, Cash Ledger, and liability ledger is updated in real-time. And other information such as – information about tax and ITC under SGST, IGST, CGST, and Cess generated automatically from the debit entries in credit cards or cash ledger. The complete process is independent of the mode you are using to file the GSTR.
- Taxpayers can also claim the refund of the payment if in case they have done excess payment on the GST portal. They can also use the excess payment in the forthcoming month.
Let’s Summarize –
We are confident now that you have understood all the information about GSTR 3 such as its filing process, its key components, the eligibility criteria, and the importance of filing it. If still there is a bit of confusion left then feel free to comment and get advice from our experts.
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who needs GSTR 3?
All the tax paying persons registered under GST have to file GSTR-3 returns. Also, every person with the payable supply of goods and services equal to or more than Rs. 20 lakhs must register under GST
What is the purpose of filing GSTR 1, GSTR 2, and GSTR 3?
GSTR-3 is a monthly return with all the details of tax liability. It also collects information for outer supplies and inner supplies and the tax paid. It is auto-populated from GSTR-1 and GSTR-2.
Can GSTR 3 be filed on a quarterly basis?
Any small taxpayer with up to Rs. 5 crore turnover in the previous financial year can quarterly pay the tax by filing GSTR 3 form.