Smart City Mission is Critical for Developing a Universal Framework.
India’s rapid urbanisation presents both an opportunity and a challenge. As cities become the epicentres of economic activity, infrastructure, and innovation, the need for smarter, more sustainable urban development has never been greater. In response to this demand, the Government of India launched the Smart Cities Mission in 2015. This ambitious initiative aims to redefine urban living through technology, efficient governance, and inclusive growth.
The Smart Cities Mission is about more than just modern infrastructure; it envisions environmentally sustainable, digitally connected, and citizen-friendly cities. From intelligent traffic management and eco-friendly waste solutions to advanced public transport and e-governance, these smart initiatives are designed to improve the quality of life for all residents. This transformative project covers 100 cities across the country, each tailored to meet the specific needs and potential of its region.
This blog explores the core objectives, features, and progress of the Smart Cities Mission, providing insights into how these cities are being shaped for a better, smarter future.
Table of contents
- What is the Smart Cities Mission?
- Features of Smart Cities Mission in India
- Smart City India’s Smart Solutions
- Financing of Smart Cities Mission in India
- Smart City List Map
- List of Cities for Smart City in India
- Smart Cities Mission India Challenge
- Other Missions Related to Smart Cities Mission
- Current Status of Smart City Mission in India
- Recommendations for Smart Cities Mission
- Smart City Mission under SCM
- Smart City Projects Success Stories
- FAQ's about Smart Cities India
What is the Smart Cities Mission?
The Smart Cities Mission is an initiative by the Government of India to improve the lifestyle of citizens living in that particular city or town. This initiative will be taken further by the best practices, information, and smart technologies. Several public-private partnership firms are also going to be a part of the Smart Cities Mission.
This mission was first launched on June 25, 2015, by Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi. Furthermore, the Union Ministry of Urban Development is in charge of executing the mission throughout the cities. A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) has also been created in each state and is headed by the CEO. It is done in order to look after the proper implementation of the Smart City projects. In order to make it a successful implementation of new age development, funding of ₹ 7,20,000 crore has been provided by the government.
After completing a five-round process, 100 cities throughout India have been selected. Development starts taking place according to the list of smart cities in India and the master plan. All the states, leaving West Bengal, have taken part in this development mission. WB is not a part of this initiative due to the difference in state and central government ideologies. Following this, Navi Mumbai and Mumbai also withdrew from Maharashtra state from the mission.
Features of Smart Cities Mission in India
The Smart Cities Mission in India is designed to address urban challenges through innovation, technology, and sustainability. Here are the key features that define the mission:
- Mixed Land Use Planning: The mission encourages land use for multiple purposes, such as residential, commercial, and recreational activities within the same area. This promotes efficient land use and reduces the need for long commutes.
- Inclusive Housing Solutions: The mission is to ensure inclusive urban development by providing affordable housing for all income groups, particularly the economically weaker sections.
- Improved Mobility and Public Transport: The mission promotes the development of integrated transport systems, including reliable public transportation, dedicated cycling tracks, and pedestrian-friendly pathways. These improvements aim to reduce traffic congestion, lower pollution levels, and provide safer travel options.
- Smart Infrastructure: Cities under the mission are equipped with smart technologies for essential services such as water supply, electricity distribution, waste management, and traffic control. These technologies enhance service efficiency, reduce waste, and ensure timely service delivery to residents.
- Environmental Sustainability: Environmental conservation is a priority within the mission. Cities are encouraged to adopt renewable energy sources, construct energy-efficient buildings, implement rainwater harvesting, and develop urban green spaces. These initiatives help promote sustainable living and mitigate environmental impacts.
- E-Governance and Citizen Participation: To increase transparency and accountability, the mission focuses on digitising government services. Citizens can access services online, lodge grievances, and engage with local authorities through mobile apps and portals.
- Safety and Security Measures: Advanced security solutions such as CCTV surveillance, smart street lighting, and emergency response systems are implemented to ensure the safety of residents. These measures help reduce crime rates and create a secure urban environment.
- Smart Solutions for Waste Management: The mission integrates innovative waste management systems, including waste-to-compost and waste-to-energy initiatives. Automated waste collection and treatment facilities are designed to maintain urban cleanliness and reduce the burden on landfills.
- Sustainable Energy Solutions: Cities are encouraged to adopt renewable energy sources such as solar power. Using smart meters to monitor energy consumption ensures efficient energy management and reduces dependency on non-renewable resources.
- Urban Livability Improvements: To improve residents' quality of life, the development of parks, open gyms, playgrounds, and other recreational spaces is prioritised. These spaces promote healthier lifestyles and provide community interaction opportunities.
- Skill Development and Economic Growth: The mission supports establishing skill development centres and trade hubs to enhance local employment opportunities. These initiatives aim to boost city innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth.
Smart Water Management: Cities implement smart water management systems, including smart meters for water usage, leak detection mechanisms, and water quality monitoring. These solutions ensure efficient water supply, conservation, and reduced wastage.
Smart City India’s Smart Solutions
Under the Smart Cities Mission, the following are the smart solutions offered by the authority for the basic construction of the infrastructure:
- Grieval redressal and public information
- Delivery of electronic services
- Eyes and ears for the city’s citizens
- Monitoring of video crimes
- Citizen engagement
- Waste to compost initiative
- Waste to fuel and energy
- Every drop treatment
- C&D waste treatment
- Smart meters
- Electricity and water management
- Identification of leakage
- Monitoring water quality
- Renewable energy source
- Green buildings
- Energy efficiency
- Smart parking system
- System of intelligent traffic management
- Integrated multi-modal transportation system
- Tele-medicine
- Centre of trade facilitation
- Skill development centres
Financing of Smart Cities Mission in India
Till now, the Government of India has accumulated funds of ₹ 7,20,000 crore. The whole cost is divided into a hundred smart cities and projects calculates to ₹ 100 crore/city in the span of five years. This scheme is being sponsored as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) and is based on the 50:50 model. This means that 50%, i.e, ₹ 50 crores will be contributed by the Central Government and the rest 50% (₹ 50 crores) will be contributed by the State Government/Union Territory. The financing has been a tough part of the Smart City projects as the Centre released ₹ 27,282 crores while the state only released ₹ 20,124 crores till November 2021.
Smart City List Map
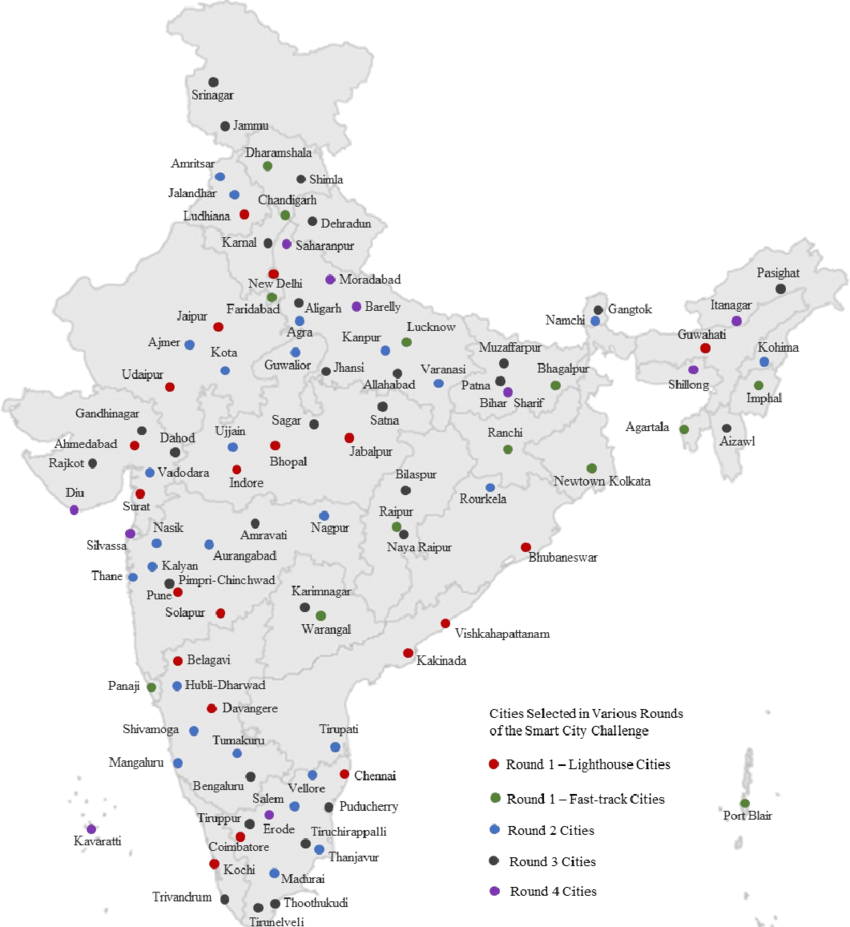
Source: researchgate.net/figure/Location-of-100-cities-selected-under-the-Smart-Cities-Mission
List of Cities for Smart City in India
The smart city list furnished by the Government of India and authorities taking part in the development are the following:
- Port Blair
- Visakhapatnam
- Tirupati
- Kakinada
- Amaravati
- Pasighat
- Guwahati
- Muzaffarpur
- Bhagalpur
- Biharsharif
- Patna
- Chandigarh
- Raipur
- Bilaspur
- Naya Raipur
- Diu Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Silvassa
- New Delhi Municipal Council
- Panaji
- Gandhinagar
- Ahmedabad
- Surat
- Vadodara
- Rajkot
- Dahod
- Karnal
- Faridabad
- Dharamshala
- Shimla
- Srinagar
- Jammu
- Ranchi
- Mangaluru
- Belagavi
- Shivamogga
- Hubballi Dharwad
- Tumakuru
- Davangere
- Bengaluru
- Kochi
- Trivandrum
- Kavaratti
- Bhopal
- Indore
- Jabalpur
- Gwalior
- Sagar
- Satna Ujjain
- Nashik
- Thane
- Greater Mumbai
- Amravati
- Solapur
- Nagpur
- Kalyan-Dombivali
- Aurangabad
- Pune
- Pimpri Chinchwad
- Imphal
- Shillong
- Aizawl
- Kohima
- Bhubaneshwar
- Raurkela
- Oulgaret
- Ludhiana
- Jalandhar
- Amritsar
- Jaipur
- Udaipur
- Kota
- Ajmer
- Namchi
- Gangtok
- Tiruchirapalli
- Tirunelveli
- Dindigul
- Thanjavur
- Tiruppur
- Salem
- Vellore
- Coimbatore
- Madurai
- Erode
- Thoothukudi
- Chennai
- Greater Hyderabad
- Greater Warangal
- Karimnagar
- Agartala
- Moradabad
- Aligarh
- Saharanpur
- Bareilly
- Jhansi
- Kanpur
- Prayagraj
- Lucknow
- Varanasi
- Ghaziabad
- Agra
- Rampur
- Dehradun
Smart Cities Mission India Challenge
The Ministry of Urban Development in India used the competition method of area-based strategy This was done for the development to select the cities that will be included under this Smart Cities Mission. The cities in the first phase of the competition competed at the state level in all the participatory cities and the winners were selected for the national level. The top cities scoring the highest in the national Smart City projects’ mission got selected for the development process. The nominations of all the participatory cities came from the Government of States.
Don't miss It!
| Smart City Dehradun | Dehradun Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Delhi | Delhi Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Bhopal | Bhopal Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Ranchi | Ranchi Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Dholera | Dholera Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
| Smart City Bangalore | Bangalore Smart Cities Projects & Mission |
Many other government-related projects are being interlinked to make this initiative a success. Integrating various components of development, i.e, social, economic, cultural, institutional, and physical, the Smart City projects aims to create a whole different world. The various sectorial schemes linked with this mission are as follows:
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) – This mission aims to provide basic services like water supply, urban transport, sewage, etc to people. It also focuses on building amenities in several cities that can help in enhancing the quality of life, especially for the poor and disadvantaged people of the country.
- Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDYA) – This mission aims to protect and preserve the heritage of the cities. It also focuses on providing inclusive heritage that can be linked with urban development by exploring various avenue sectors that includes the private sector too.
- Digital India – Creating a digital infrastructure is the aim of Digital India's mission. This includes digital delivery of services, digital literacy and others. The mission focused on developing and ameliorating digital infrastructure in every corner of the country.
- Make in India – The main objectives of the Make in India mission are to foster innovation, promote and facilitate investment, protect intellectual property rights, enhance the development of skills, and build the state-of-the-art infrastructure for manufacturing in the country.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – The PMAY aims to provide central assistance to the people through the implementing agencies in all the States and Union Territories of India to provide housing solutions to eligible families and beneficiaries.
- Swach Bharat Abhiyan – The aim of this mission is to reduce and eliminate open defecation throughout the country.
Current Status of Smart City Mission in India
The status of the Smart City India mission according to the data furnished by the relevant authority as of February 16, 2022, are as follows:
| Particulars | Numbers |
| Cities | 100 |
| Projects | 5151 |
| Amount | ₹ 2,05,018 crore |
| Tendered | 6809 Projects / ₹ 189,737 crore |
| Work orders issued | 6222 Projects /₹ 164,888 crore |
| Work completed | 3480 Projects /₹ 59,077 crore |
Recommendations for Smart Cities Mission
Here is a list of some recommendations that can help the Smart Cities Mission become successful and achieve more advantages:
- This should be termed as a long-term mission instead of being a five-year programme. This is because the longer span will help in performing better which is not possible in just five years.
- The government should identify more missions to interlink them with the Smart City projects to achieve great results. Linking with other projects can help in dealing with more issues and can easily resolve the issue faced by the cities.
- Research and findings should be done in order to know why particular projects are not being carried out. Some of these cities are Muzaffarpur, Shillong, Bhagalpur, and Amravati.
- The authorities should generate more funds through taxation for the amount to mobilise. Moreover, the transfer of funding can also be made accessible for development.
- Cybersecurity should be a major part of the development for providing safety to the cities under this project. This will ensure encrypted data security and can’t be easily breached.
Smart City Mission under SCM
The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs’ Smart Cities Mission is soon to launch another strategy, known as ‘DataSmart Cities’. This new strategy will help the authorities take up the data which will assist in solving complex urban problems. Under this new initiative of the Smart City list in India, the focus will be on the advancement of data-driven governance.
This new initiative of DataSmart Cities will also encourage areas to incorporate the data culture fundamentals at their local levels. These can include forming Smart Cities, an alliance of these cities, data strategy of the city, a network of the smart cities, and many others. This new initiative will also promote peer-to-peer learning throughout the city about data-driven governance. It outlines the reusable cases related to smart city development in multiple fields.
Smart City Projects Success Stories
Being a highly anticipated initiative, the Indian Government and the Ministry of Urban Planning gave great results. Some of the success stories of the Smart City list that made headlines are as follows:
Data Centre Strengthening and Disaster Recovery (DR) Site
The Indian Government along with its Corporate Partners has launched multiple e-governance initiatives. Smart City projects, and other projects in order to meet the citizens' demands for online services. In the past few years, requirements for data centre has been growing without bounds. In order to meet that, the Surat Municipal Corporation (SMC) has envisioned building up the data centre and Infrastructure for Data Recovery.
Automatic Fare Collection System (AFCS) in Surat
Being one of the fastest-growing cities in India and the world, Surat ranked fourth in the list of developing areas. With a wide range of business sectors ranging from textile to real estate, this city is full of career opportunities. With development, the city also started attracting many people for business, jobs, education etc. This calls for a better system and heavy traffic at the same time. In the last three years, the city went through multiple substantial changes like an automatic collection of public transport fares.
The Surat Municipal Corporation (SMC) introduced an advanced public transportation system with the help of the Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS). The 30 kilometres route went through the advancement in Phase I of the change, which added further 42 kilometres in the next phase. This new smart initiative made it easy for both travellers to pay and authorities to collect fares without any hassle. The SMC has a master plan to include 2,000 public city buses and 300 BRTS buses to comply with this new system in the upcoming three years.
Visakhapatnam’s Smart Streets
Visakhapatnam got their smart streets under the Smart Cities Mission. The pilot construction project includes 7 kilometres of two major streets of the city. These roads are Waltair Road and Chinna Waltair Road. Under this project, wide roadways, cycling ways, pedestrian lighting, landscaped corridors, tree plantation, and other factors are being focused on.
Latest and Important Updates On Smart Cities Mission
Smart Cities Mission Extended Until 2025
The Government of India has extended the Smart Cities Mission until March 31, 2025, to allow for the completion of ongoing projects and ensure the full realisation of the mission’s goals.
Project Completion Status
As of November 2024, 91% of the projects under the Smart Cities Mission have been completed. Out of the 100 designated smart cities, 13 cities have completed all their planned projects, while 48 cities are in the final stages of completion.
FAQ's about Smart Cities India
Q1. Which is the number one smart city in India?
Bhopal has been given the top spot for the Smart Cities Mission in India in 2022 after an assessment by the Union Ministry of Housing and Concrete Affairs.
Q2. What is the smart city concept in India?
The main purpose of the Smart City India mission is to drive economic growth and help in improving people’s lifestyle quality with the development of local areas. This development is taking place by harnessing smart technology.
Q3. How many smart cities are in India?
Currently, there are about 100 smart cities in India, according to the Union Ministry of Housing and Concrete Affairs.
Q4. Why do we need smart cities in India?
Smart Cities in India are important to develop and promote economic growth, and enhance the quality of life with the use of smart technology.
Q5. How do smart cities help the environment?
Smart cities are the smart way to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through vehicles. The plans also reduce the electricity and heat produced by the transport sector.




